Published/Posted: May 20, 2024
Authors: Joint, François; Zhang, Kunyi; Poojali, Jayaprakash; Lewis, Daniel; Pedowitz, Michael; Jordan, Brendan; Prakash, Gyan; Ali, Ashraf; Daniels, Kevin; Myers-Ward, Rachael L.; Murphy, Thomas E.; Drew, Howard D.
arXiv: 2405.06579
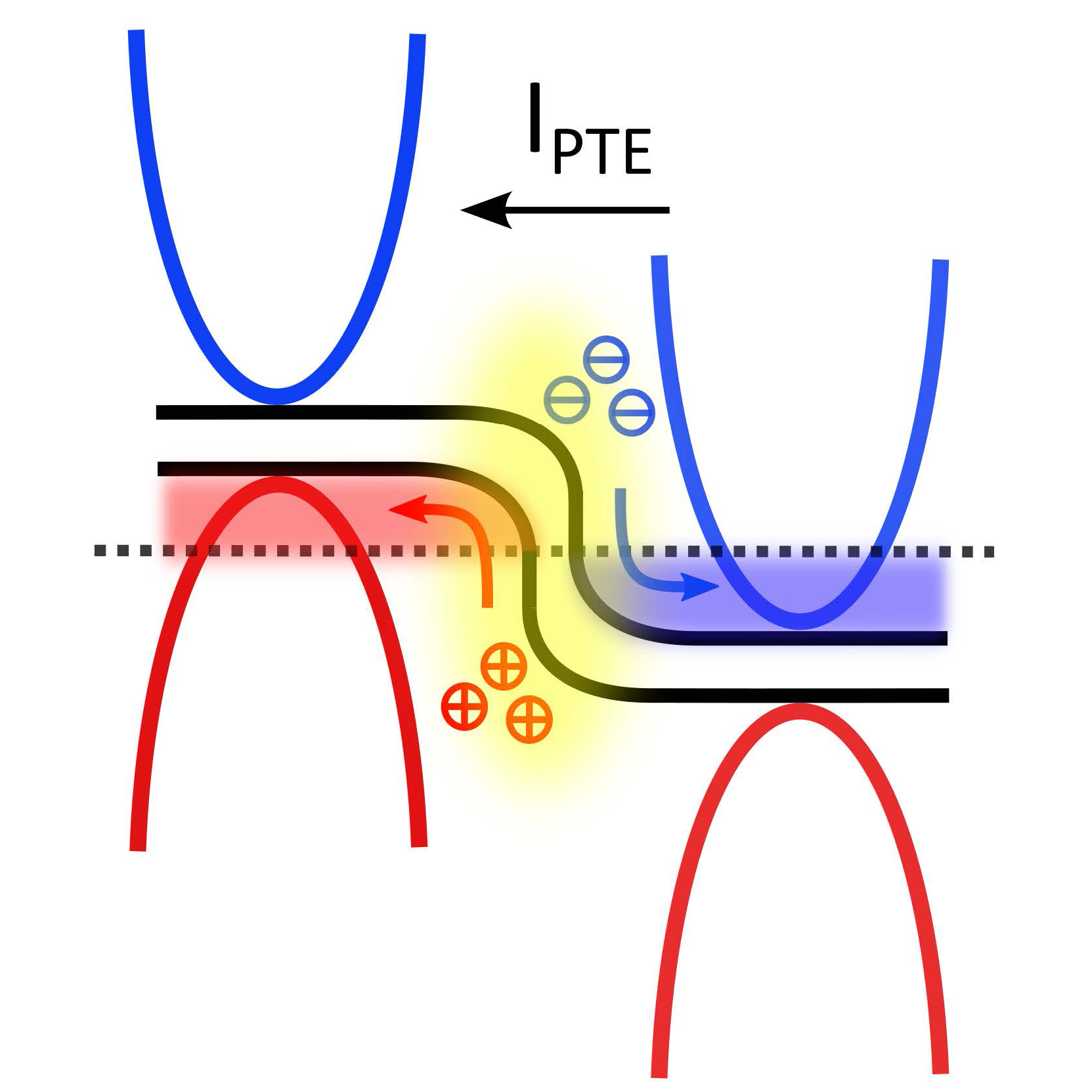
Abstract: Developing low-power, high-sensitivity photodetectors for the terahertz (THz) band that operate at room temperature is an important challenge in optoelectronics. In this study, we introduce a photothermal-electric effect detector based on quasi-free-standing bilayer graphene on a silicon carbide substrate, designed for the THz frequency range. Our detector’s performance hinges on a quasi-optical coupling scheme, which integrates an aspherical silicon lens, to optimize impedance matching between the THz antenna and the graphene p–n junction. At room temperature, we achieved a noise equivalent power of less than 300 pW/Hz^1/2. Through an impedance matching analysis, we coupled a planar antenna with a graphene p–n junction, inserted in parallel to the nanogap of the antenna, via two coupling capacitors. By adjusting the capacitors and the antenna arm length, we tailored the antenna’s maximum infrared power absorption to specific frequencies. The sensitivity, spectral properties, and scalability of our material make it an ideal candidate for future development of far-infrared detectors operating at room temperature.Citation:
F. Joint, K. Zhang, J. Poojali, D. Lewis, M. Pedowitz, B. Jordan, G. Prakash, A. Ali, K. Daniels, R. L. Myers-Ward, T. E. Murphy and H. D. Drew, "Terahertz Antenna Impedance Matched to a Graphene Photodetector", 6(6) 4819-4825 (2024)
Export: BibTeX | RIS
Manuscript: Joint_ACSApplElectronMat_6_4819_2024.pdf